Fuselage : It is the central portion of the body of an airplane,designed to accommodate the crew,passengers and cargo. The Fuselage must be strong ans streamlined since it must withstand the forces that are created in flight. Five types of stress act on an airplane fuselage in flight. They are tension,compression,bending,shear and torsion. Fuselage extends from the nose to tail of the airplane. the wings and the tail are attached to the fuselage. The part of the pilot compartments is called cockpit or flight deck.
The fuselage could be pressurized or non pressurized . The fuselage of pressurized aircraft has additional capacity to withstand structural load and the pressure differences between high cabin pressure and low outside atmospheric pressure. The pressurized aircraft can fly at very high altitude (low atmospheric pressure) with low altitude(higher) atmospheric cabin pressure for the comfort of passengers.
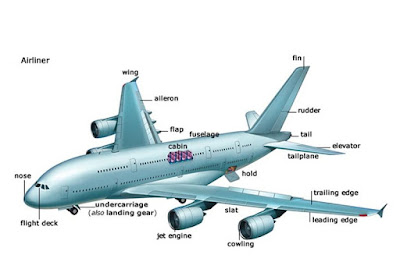 |
| Parts of Airplane: Source |
Wing: The cross section of the wing of an airplane is shaped like an airfoil and generates lift. It is attached rigidly to the fuselage. It extends outward from each side of the fuselage. It is nearly flat on the bottom and curved on the top. The top surface of the wing is more critical surface and generates lift. Thus,airplane carries the engines under the wing but not on top where they would interfere with lift.
The high wing airplane the wing is placed on high above the fuselage. Mid wing positioned in the middle of the fuselage. Low wing is placed below the fuselage. The ailerons,flaps,slats and spoiler are attached to the both sides of the wings. Except in some T-tail aircraft,the engines are attached to the wings. The main fuel tanks are also generally located inside the hollow space of the wings.
Shape and Size of the Wings:
- The Straight (Rectangular) Wing: It has its leading edge is at almost at right angle to the fuselage.
- The Tapered Wing: It has round leading edge and or trailing edge.
- The Sweep Back Wing: It has its leading edge at slant back from root to tip of the wing. It is used on high speed jet aircraft.
- Forward Sweep Wing: It has its leading edge swept toward the front of the airplane.
- The Delta Wing : It is shaped like triangle which has the root almost as long as fuselage and leading edge is sharply swept back.
- Variable Swing Sings: It can vary the sweep of their wing in flight.
Using the computer and wind tunnel experiment, the performances of different shape and sizes of wings area evaluated for the particular airplane requirements. The shape and size plays the very important role, on fuel consumption,speed,payload etc
Tail (Empennage): It is the rear part of the airplane. It consists of vertical stabilizer or fin and horizontal stabilizer. Rudder is attached to the vertical stabilizer(fin) and elevators are attached to the horizontal stabilizer. The trim tabs are attached to the ailerons,rudder and elevators.
Landing Gear or Undercarriage: Landing gear is the part of an airplane that supports the aircraft weight on the ground. It includes wheels,shock absorbers and support struts. There is a landing gear unit under the nose of the aircraft as well as approximately midway back,under the fuselage or near the root of the wings. Landing gear normally includes rubber tires,but may have skis for landing on snow or floats for landing on water.
The front wheel is called the nose wheel. The nose wheel is used for taxing. Rear wheels are called main wheels. The big jests like B-747 and A380 have multiple landing gears. Each landing gear assembly carries 4 to 6 wheels. Some small airplane has main wheels on the front and small wheel on the tail like Pilatus Porter.
 |
| Landing Gear |
 |
| Nose Wheel and Landing Gear |


No comments:
Post a Comment